MORE NIMBLE & EFFICIENT OPERATIONS

The Internet of Things (IoT) is poised to impact virtually every industry, but none more so than manufacturing. In fact, IoT may be the biggest driver of change in factories and other facilities, unlocking Industry 4.0.
5 minute read
● New levels of speed, efficiency, and performance are helping create new use cases for IoT.
● By 2024, the Industrial IoT market is expected to grow by 42.7%.
● 5G and IoT are improving five main areas of Industry 4.0: supply chain management, product quality, predictive maintenance, production efficiency, and digital twins.
As in other sectors, IoT and Industrial IoT related to manufacturing are made possible by wireless connectivity and the technologies that support it. Today, IoT relies on low power and long range, which the Narrowband (NB) standard addresses. NB connections can support a variety of IoT use cases including event detectors, smart trash bins, and smart meters. Industrial applications include asset and logistics tracking, machine monitoring, and more.
But as nationwide 5G connectivity continues to develop, an entirely new level of speed, efficiency, and performance will help create new IoT use cases.
5G will be necessary for higher data rate transmissions and ultra-low latency needs. In fact, a report from Bloor Research indicates that the future of 5G, edge computing, and IoT combined are key enablers for Industry 4.0.


According to a report from Markets and Markets, Industrial IoT is expected to grow by 42.7% over the 5-year period ending in 2024. Among the major factors driving this growth are more advanced semiconductor and electronic devices, and an increase in cloud computing platforms—both of which the 5G era is expected to drive.
Without 5G, there will be significant network gaps to enabling Industry 4.0—not only in providing connectivity for billions of devices but also in processing the enormous amount of data that will be generated.
The challenge isn't simply about bandwidth, though. Different IoT systems will have different network requirements. Some devices will demand extremely high reliability where low latency will be critical, while others will force networks to cope with a much higher density of connected devices.
For example, at a production plant, someday simple sensors might collect and store data and communicate to a gateway device that contains application logic. In other situations, IoT sensor data might need to be collected in real-time from a variety of sensors, RFID tags, tracking devices, and mobile devices across a wider area via 5G protocols.
Bottom line: 5G in manufacturing has the power to help unlock a variety of IoT and Industrial IoT use cases and benefits for Industry 4.0. Looking ahead, don’t be surprised if you see these five use cases transform with strong, reliable connectivity from multi-spectrum 5G networks and the introduction of compatible devices.
With IoT and Industrial IoT, manufacturers can connect production equipment and other machines, tools, and assets in factories and warehouses, giving managers and engineers greater visibility into production operations and unprecedented insights into potential issues.
One of the key capabilities of IoT is asset tracking, or the ability to easily locate and monitor key components of a production facility. In the (near) future, companies will be able to automatically track parts as they move through the assembly process using smart sensors. Plant managers will also gain a real-time view of production output by connecting tools used by operators with the machines used in production.
With IoT-generated data, manufacturers will have the power to leverage greater levels of visibility within plants to quickly identify and resolve bottlenecks. 5G will help power smart dashboards, which will lead to faster, higher quality production.
A single malfunction can lead to significant production delays, which can result in heavy losses, unexpected equipment repair or replacement. It can also make customers unhappy due to delayed or canceled orders. When efficiency matters, it's critical to ensure that factory equipment and other assets are in good working order.
5G can help here by connecting wireless sensors deployed on machines throughout a factory, letting managers detect when a specific piece of equipment is beginning to malfunction before it shuts down completely.
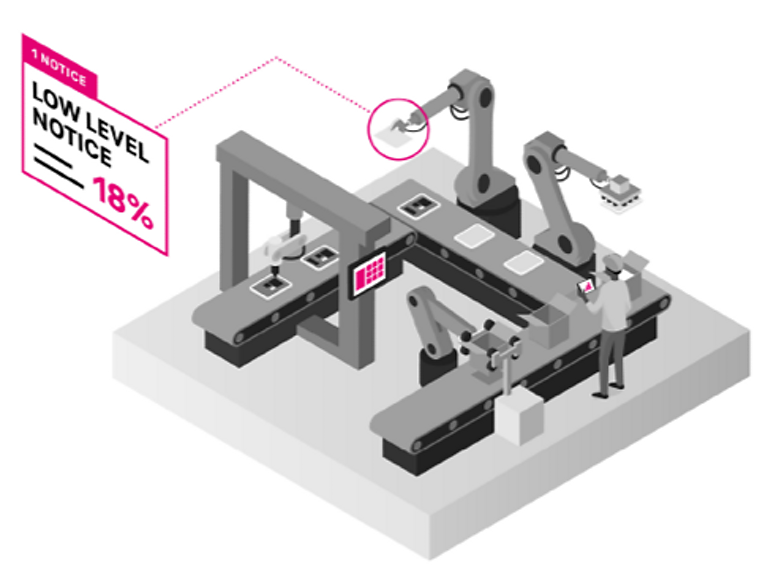
Emerging and integrated IoT systems supported by 5G can sense warning signs in equipment and send alerts to maintenance staff who can proactively repair machines. In addition, manufacturers can potentially run safer plant environments and enjoy longer equipment lifespans.
Continuously monitoring products throughout the building cycle can help manufacturers improve their quality because environmental sensors actively send data about equipment conditions.
5G comes in again here—powering sensors that can alert supervisors whenever quality thresholds are reached or when conditions such as air temperature or humidity are not optimal for specific items, such as foods or pharmaceuticals.
Manufacturing supply chains are becoming increasingly complex, especially for organizations with global operations. 5G allows companies to seamlessly monitor events across their supply chains, delivering real-time data through asset tracking—including trucks, shipping containers, and even individual products.
Manufacturers can use sensors to track and monitor inventories as they move from location to location throughout the chain. That includes shipments of supplies, making products, and the delivery of finished goods. Manufacturers can also gain increased visibility into product inventories and more accurately forecast shipment timelines.
Emerging IoT allows manufacturers to create digital twins—virtual replicas of physical devices and products—that can run simulations before devices are built and deployed. Because of the higher bandwidth 5G affords, streams of real-time data allow manufacturers to detect flaws sooner and more accurately predict outcomes.
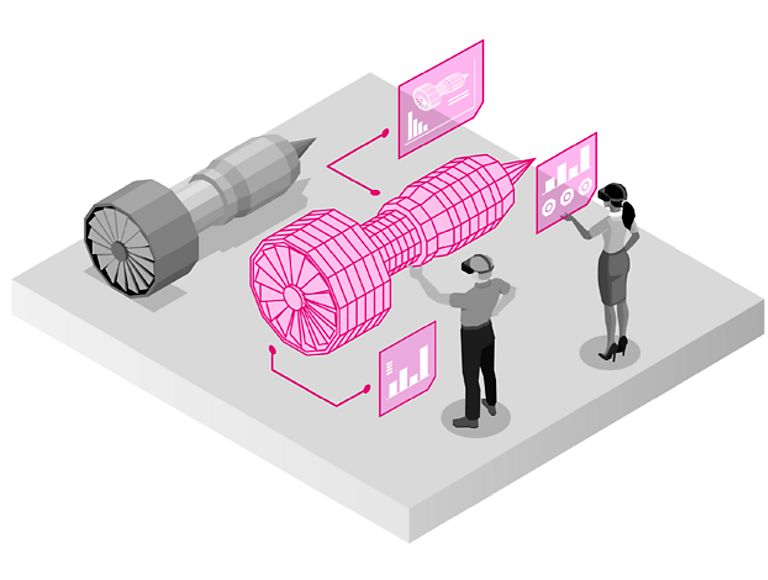
Those types of efficiencies can lead to higher-quality products and reduce costs associated with recalling products after they've been shipped. In addition, data collected from digital replicas can help managers analyze how well systems work under various conditions in the field.
With a range of potential applications, each of these five prospective use cases has the power to revolutionize the manufacturing sector. To make the most of what Industry 4.0 technology can do for their operations, leaders within manufacturing will need to understand the opportunities presented by IoT and learn how 5G can bring them to life.
Ready to start building your 5G future?